
What if the population standard deviations are known? If the samples are related (for example, you are comparing the answers of husbands and wives, or identical twins), you should use a This is because the samples are not related with each other, in a way that the outcomes from one sample are unrelated from the other sample. Why is it called t-test for independent samples?
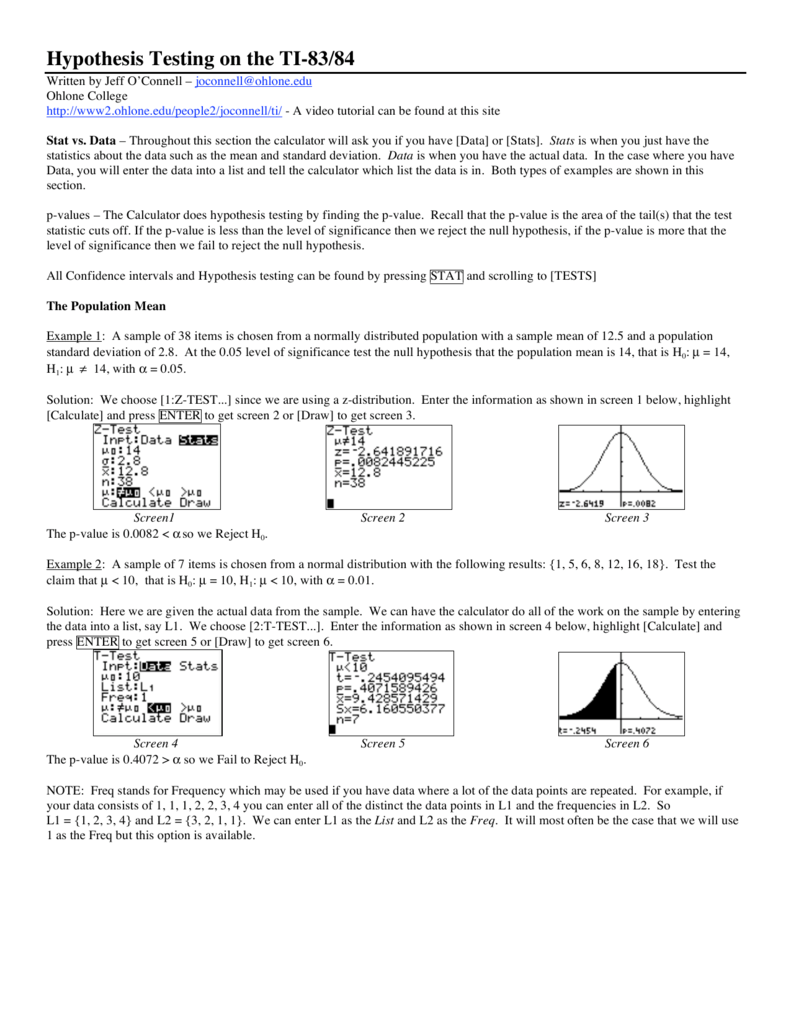
With the above t-statistic, we can compute the corresponding p-value, which allows us to assess whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between two means. Normally, the way of knowing whether the population variances must be assumed to be equal or unequal is by using an F-test for equality of variances. If the population variances are assumed to be unequal, then the formula is: The formula for a t-statistic for two population means (with two independent samples), with unknown population variances shows us how to calculate t-test with mean and standard deviation and it depends on whether the population variances are assumed to be equal or not.
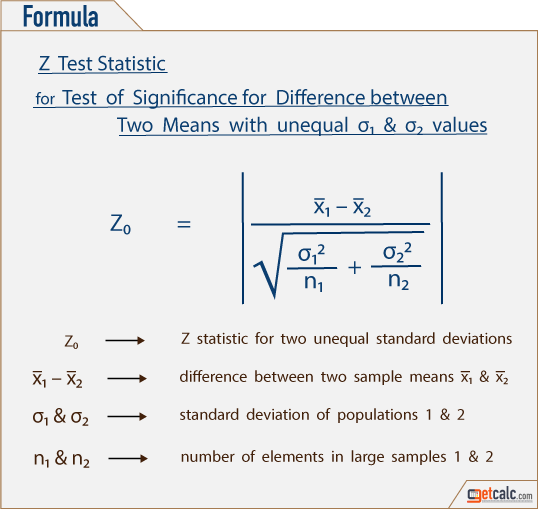
How do you compute the t-statistic for the t test for two independent samples? Type I error occurs when we reject a true null hypothesis, and the Type II error occurs when we fail to reject a false null hypothesis In a hypothesis tests there are two types of errors. The p-value is the probability of obtaining sample results as extreme or more extreme than the sample results obtained, under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true The main principle of hypothesis testing is that the null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic obtained is sufficiently unlikely under the assumption that the null hypothesis The main properties of a two sample t-test for two population means are:ĭepending on our knowledge about the "no effect" situation, the t-test can be two-tailed, left-tailed or right-tailed

The null hypothesis is a statement about the population means, specifically the assumption of no effect, and the alternative hypothesis is the complementary hypothesis to the null hypothesis. The test has two non-overlapping hypotheses, the null and the alternative hypothesis. More specifically, a t-test uses sample information to assess how plausible it is for the population means \(\mu_1\) and \(\mu_2\) to be equal. So you can better interpret the output presented above: A t-test for two means with unknown population variances and two independent samples is a hypothesis test that attempts to make a claim about the population means (\(\mu_1\) and \(\mu_2\)).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
